Above that, in the heart, is the charming lotus of the shining color of the bandhuka flower…It is known by its name of anahata, and is like the celestial wishing-tree, bestowing even more than what one desires…
Description of the Six Centres, Verse 22
Anahata – the heart chakra
When we want to demonstrate that something is meaningful or personal to us, we tend to spontaneously gesture to the center of our chest. Our atma (the essence of our true self) resides here in the anahata chakra, the heart center, much in the same way that the essence of an entire tree resides within one seed.
Anahata in Sanskrit means unhurt, unstruck, or unbeaten. The word is a “sound produced without touching two parts.” This refers to the concept of the sound of the celestial realm described in Vedic texts, the oldest known Hindu scriptures. Rather than two forces coming together in opposition, they co-exist without conflict, there is synergy and cooperation. We are able to experience things with a detached perspective, to “follow our heart,” to make decisions based on our higher self, not karma or emotions.
The location of anahata means that it affects not only the heart but the lungs, chest, arms, and hands. Having a blockage or imbalance in this chakra can manifest itself physically in respiratory or circulatory issues. Mental/behavioral symptoms may include co-dependence, manipulative behaviors, feeling unworthy, people pleasing, and/or antisocial behavior.
When anahata is activated and open, it is associated with love and compassion, charity to others and psychic healing. The more that the heart center opens, the more strongly and deeply we feel. This may reveal some past hurts, but by working through these feelings, we are able to let them go. Then we can access feelings of balance, calmness, and serenity and free ourselves from being bound to our emotions.
Although anahata is commonly represented by the color green these days, it has also been described as light blue, representing spirituality and unity, and symbolizing the purification resulting from the fire of manipura (think the blue center of a flame). The mandala for anahata is said to be surrounded by twelve red lotus petals.
In the middle of the mandala is a six-pointed star, formed by two intersecting triangles, highlighting the inner battle between spirituality and emotion. The center of the star is described as having a smoky color and containing a representation of a new moon, which relates to changeability we experience in this chakra.
The element for anahata is air. Think about how the heart is located within the region of the lungs and how closely the activities of the two organs are associated (for example, you might focus on breathing more slowly to calm your heart rate). Air symbolizes our connection to everything we encounter. It is also a force that has the ability to destroy (like a tornado) or can be utilized in a productive manner (like how the Bernoulli effect enables airplanes to fly).
Relating to the idea of air is the animal symbol for anahata, the black antelope. An antelope is fleet, shy, elusive, and graceful. For Jung the antelope symbolizes the efficiency and the lightness of our thoughts and feelings in the anahata chakra.
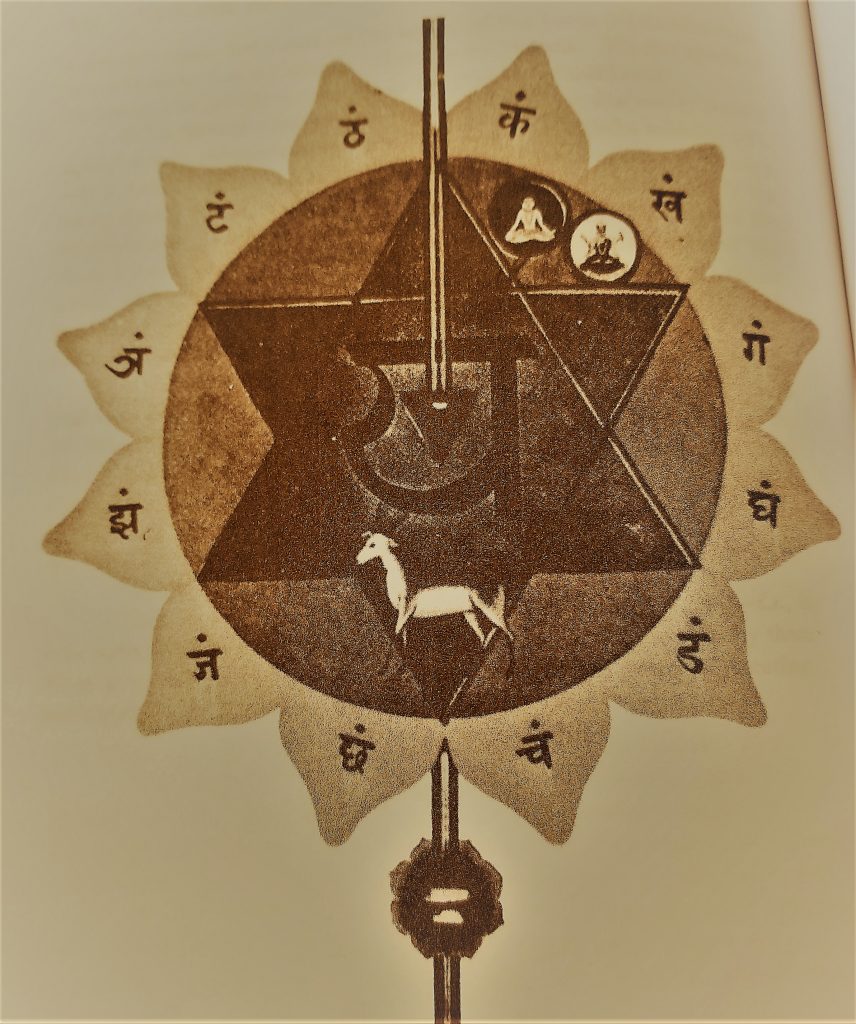

The seed syllable of anahata is “yam” which means to let go, to liberate, to give.
Jung describes anahata as the point that we become conscious of something which is not personal. We are able to separate ourselves from our emotions. Anahata serves as a bridge between lower and upper chakras, integrating the manifest with the spiritual. The first step in self-realization, recognizing one’s self in every living being – accessing the atma – happens in anahata.